Unlocking Self-Awareness: The Essential Guide to Knowing Yourself Better
When you are self aware, you can see where your thoughts and emotions are guiding you
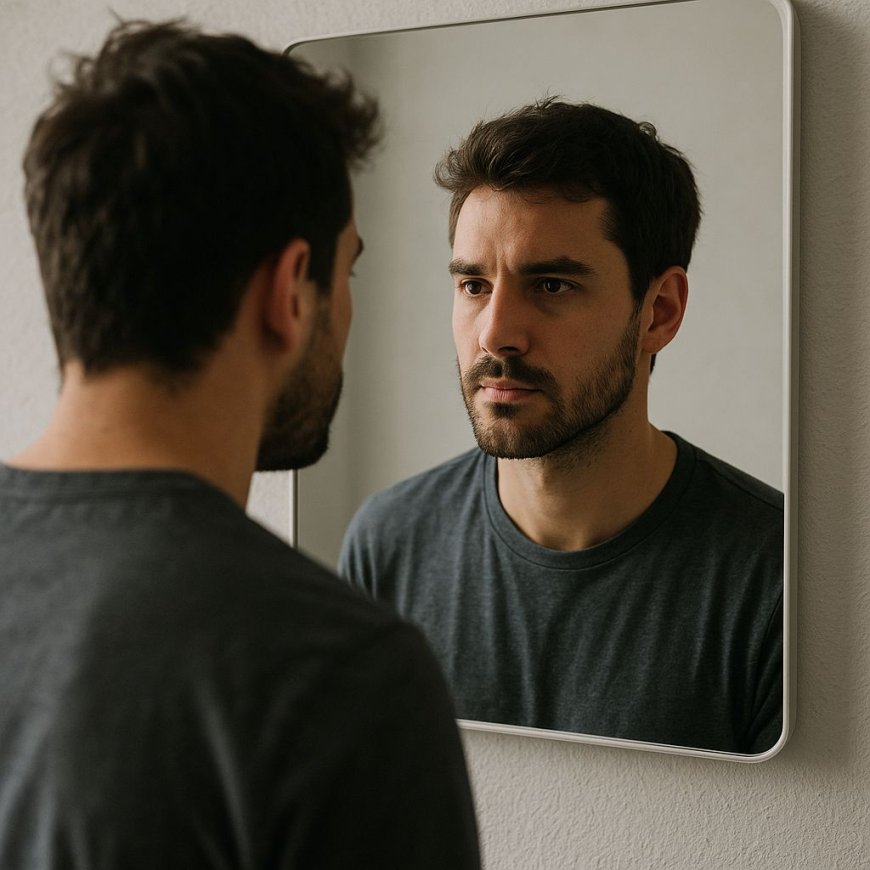

Self-awareness is the capacity to recognize and understand the unique aspects that define you as a person such as your personality, behaviors, values, beliefs, emotions, and thoughts. It’s a mental state where you consciously direct attention inward to reflect on yourself.
Although self-awareness plays a key role in shaping your identity, it’s not something you constantly think about. Rather, it becomes a natural part of who you are and shows up in different ways depending on the circumstances and your individual personality.
How Does Self-Awareness Develop?
Self-awareness is among the earliest aspects of self-concept to appear, but it doesn’t develop all at once. While people aren't born fully self-aware, research shows that even infants possess a basic or early form of self-awareness, which gradually grows and becomes more defined with time and experience.
Infants begin to show signs that they understand they are distinct from others. For example, behaviors like the rooting reflex where a baby turns its head in search of a nipple when touched on the cheek suggest this early awareness. Research also indicates that even newborns can tell the difference between touch from themselves and touch from others.
As they grow, a more advanced level of self-awareness starts to emerge around 12 months and becomes significantly more developed by about 18 months of age.
Self-Awareness and the Mirror Recognition Task
Researchers often study self-awareness using the "mirror self-recognition task". A well-known version of this experiment was carried out by Lewis and Brooks-Gunn. In their study, a red dot was placed on an infant’s nose without the child noticing. The infant was then placed in front of a mirror.
If the child recognized their reflection as themselves, they would typically reach for their own nose rather than the mirror image. This simple yet powerful reaction indicated that the child had developed a certain level of self-awareness.
It’s important to understand that the Lewis and Brooks-Gunn study mainly highlights visual self-awareness in infants. However, self-awareness isn’t limited to recognizing one’s reflection. Even at a very young age, children may show other forms of self-awareness. For instance, the way infants express emotions can reflect an emerging sense of self and an awareness of how they relate to others around them.
Self-Awareness and the Brain
Scientists believe that a part of the brain called the anterior cingulate cortex, found in the frontal lobe, plays a key role in developing self-awareness. Brain imaging studies have shown that this region becomes active when adults reflect on themselves or experience self-awareness.
Interestingly, the emergence of self-awareness in children around 18 months old, as seen in the Lewis and Brooks-Gunn study aligns with a rapid increase in spindle cells in this part of the brain. This connection suggests that the brain’s development is closely tied to how and when self-awareness begins to form.
However, one study found that a patient retained self-awareness even with extensive damage to areas of the brain including the insula and the anterior cingulate cortex.
Levels of Self-Awareness
So how exactly do children become aware of themselves as separate beings? One major theory of self-awareness, introduced by developmental psychologist Philippe Rochat, suggests that there are five levels of self-awareness. Children progress through these stages between birth and approximately age 4 or 5
Differentiation: A baby begins to acknowledge their own reflection. They may detect there is something different or special about looking at their reflection.
Situation: A baby begins to recognize their own reflection, being, and movements as separate from those around them.
Identification: This is the stage during which a child fully knows that it is their own reflection in a mirror. They know, "This is me."
Permanence: They have a complete sense of themselves and can identify themselves in pictures or videos, even as their appearance changes.
Self-consciousness: A child adapts a third-person point of view of themselves; they become aware of the idea that others perceive them in certain ways. This may result in feelings such as pride or shame.
Types of Self-Awareness
Self-awareness also takes different forms that can emerge in different situations and settings. Psychologists often break self-awareness down into two different types, either public or private.
Public Self-Awareness
This type emerges when people are aware of how they appear to others. Public self-awareness typically emerges in situations when people are at the center of attention.
This type of self-awareness often compels people to adhere to social norms. When we are aware that we are being watched and evaluated, we often try to behave in socially acceptable and desirable ways.
Public self-awareness can also lead to evaluation anxiety in which people become distressed, anxious, or worried about how they are perceived by others. Performance anxiety and social anxiety are two examples of how public self-awareness can sometimes lead to worry and distress about how other evaluate us.
Public Self-Awareness Examples
You may experience public self-awareness in the workplace, such as when you're giving an important presentation or when telling a story to a group of friends. Because you are the focus of attention, you become more acutely aware of how others might perceive you.
Private Self-Awareness
This type happens when people become aware of some aspects of themselves, but only in a private way. For example, seeing your face in the mirror is a type of private self-awareness.
Certain strategies can help you build a greater sense of private self-awareness. For example, journaling, meditating, and practicing mindfulness can help you become more aware of your inner thoughts, feelings, and sensations.
Private Self-Awareness Examples
Feeling your stomach lurch when you realize you forgot to study for an important test or feeling your heart flutter when you see someone you are attracted to are also examples of private self-awareness.
Why Is Self-Awareness Important?
Self-awareness is important because it allows you to reflect on aspects of yourself. As you understand your abilities and tendencies, your self-awareness also allows you to think about how you interact with others and the world around you.
Self-aware people are able to manage their behaviors and adapt to situations. They can accurately evaluate what the situation requires and then modify their actions accordingly.
This can be vital in many areas of life, including your relationships and work. It can also factor in when it comes to personal development. As you become more aware of your strengths and weaknesses, you can take steps to capitalize on the things you are good at and explore ways to improve the areas where you might struggle.
How to Improve Your Self-Awareness
So how do you grow self-awareness? There are many ways you can practice being present with yourself and your emotions, which, in turn, can help improve your self-awareness
Meditation
Meditation can be an especially useful practice because you don't have to worry about changing anything—simply noticing what happens during a meditation can bring greater awareness of your thoughts and feelings.
Maybe you notice that you hold tension in your body by clenching your jaw, for instance, or that you tend to worry so much about the future that it's hard to be in the present moment. This is all valuable information that can help you get to know yourself and your tendencies.7
Journaling
Journaling is a practice of self-reflection that can help you notice how you think and behave and even which areas in your life you may wish to improve. It can be a therapeutic way to gain insight into your life events and relationships.8
Talk Therapy
During therapy such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) a therapist works with you to address negative thought patterns or behaviors.
By understanding the underlying cause of your negative thoughts, for instance, you're in a more advantageous position to change them and use healthy coping mechanisms instead.
Develop Your Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness and emotional intelligence (EQ) go hand in hand. EQ refers to a person's ability to perceive their own emotions and those of others. Someone with a high EQ can effectively respond to emotions with empathy and compassion.10
Of course, no one is perfect, and EQ is a skill like any other. But by learning to express your emotions in a healthy way and practicing active listening in your relationships, you're contributing to the expansion of your self-awareness as well.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0